- Home
- Erta Ale Volcano – Ethiopia Gateway to the Earth’s Fire
Erta Ale Volcano – Ethiopia Gateway to the Earth’s Fire
Explore the otherworldly beauty of Erta Ale Volcano in Ethiopia’s Danakil Depression. Witness the mesmerizing active lava lake at the summit crater.
Nestled in the Afar region of Ethiopia, the Erta Ale volcano stands as a mesmerizing gateway to the Earth’s fiery depths. Known for its continuously active lava lake, Erta Ale is one of the most impressive and awe-inspiring natural wonders in the world. The volcano, also known as Ertale Ethiopia, offers adventurers a unique opportunity to witness the raw power of nature up close. Trekking to the summit of Erta Ale is a challenging yet rewarding experience, with the glowing lava creating a surreal and unforgettable sight. Join us as we explore the majesty of Erta Ale, the Ethiopia volcano that captivates all who gaze upon it.
Geographical Overview

Location and Landscape
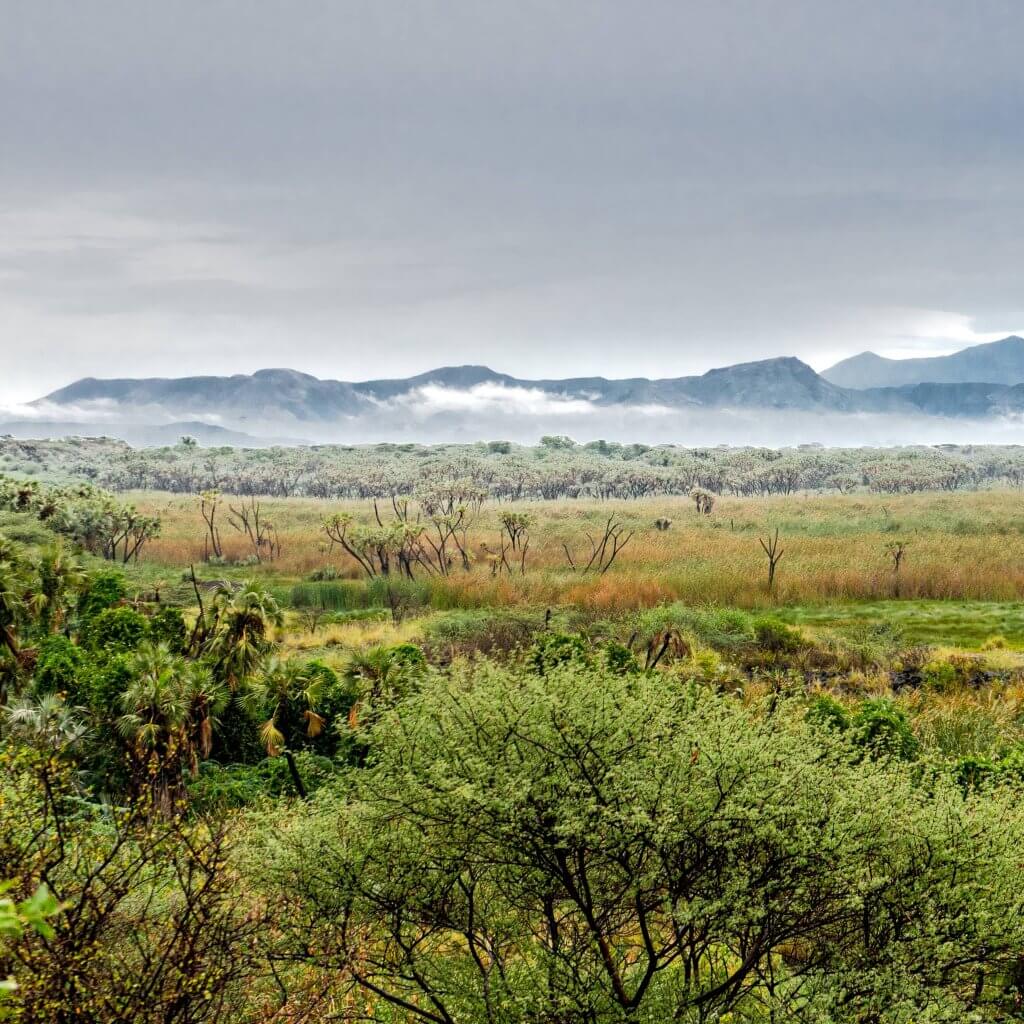
Erta Ale, located in the Afar Region of northeastern Ethiopia, is part of the Danakil Depression, one of the hottest and most inhospitable places on Earth. This volcanic region, known for its extreme heat and harsh environment, lies about 600 meters below sea level. Erta Ale is approximately 50 kilometers from the Eritrean border and is characterized by its active lava lake, one of only a few in the world. The surrounding landscape is dominated by vast lava fields, salt flats, and occasional geothermal features, creating a unique and otherworldly terrain that attracts scientists and adventure seekers alike .
Geological Characteristics
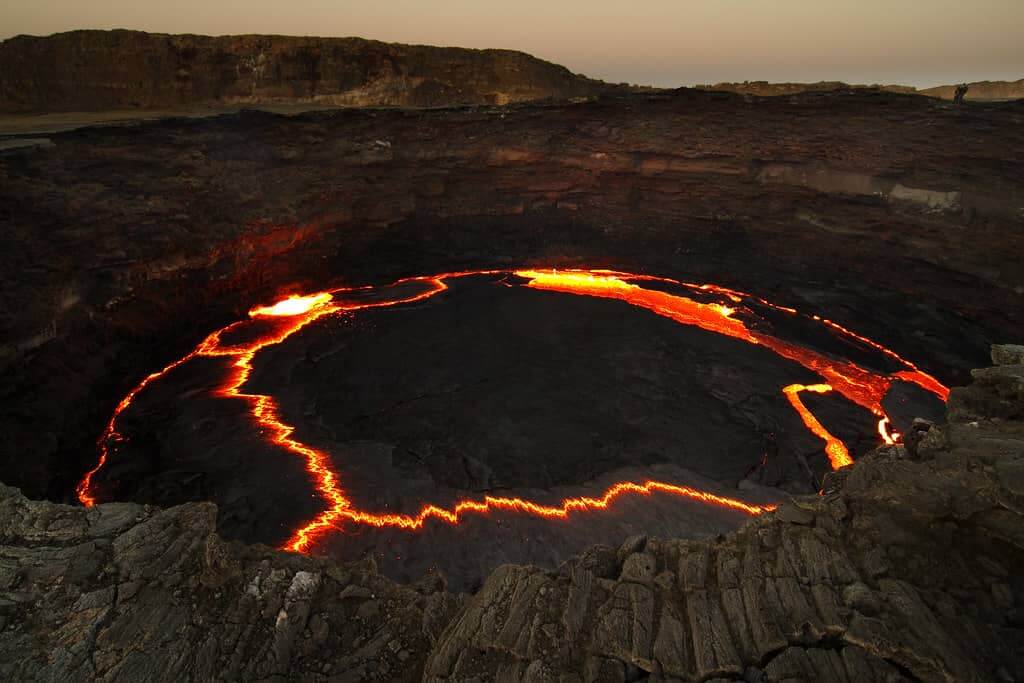
Erta Ale is a basaltic shield volcano, meaning it has gentle slopes built up by the flow of low-viscosity basaltic lava. This type of volcano typically forms large, broad domes, as seen with Erta Ale. The summit caldera of Erta Ale, about 0.7 by 1.6 kilometers in size, houses a continuously active lava lake, which has been in a persistent state of eruption since at least 1967, and possibly since 1906 .
The volcano’s activity is part of the East African Rift system, where the African and Arabian tectonic plates are slowly moving apart. This rifting process creates a significant amount of geological activity, including fissure eruptions, where magma escapes through long cracks in the earth’s crust. Erta Ale’s eruptions often involve lava flows from these fissures, which can extend several kilometers from the summit caldera. The 2017 eruption, for example, involved new fissures opening on the southeastern flank, producing extensive lava flows that overflowed the caldera’s rim .
The lava lake at Erta Ale is particularly notable for its persistent activity, providing valuable insights into the dynamics of basaltic shield volcanoes. The lake’s surface is often covered with a thin crust that continually forms and breaks apart, revealing the molten lava beneath. This constant churning and circulation of lava are due to the upwelling of magma from deep within the earth, driven by the immense heat and pressure of the planet’s interior .
Historical Activity erta ale volcano
Historical Activity erta ale volcano
Erta Ale, known as one of Ethiopia’s most active volcanoes, has a long history of volcanic activity. This basaltic shield volcano, located in the Afar Region, is renowned for its persistent lava lake and frequent eruptions. Here, we delve into some of the significant eruptions that have shaped Erta Ale’s geological landscape.
The 1906 Eruption
One of the earliest recorded eruptions of Erta Ale occurred in 1906. This eruption marked the beginning of the volcano’s modern eruptive phase, characterized by continuous lava lake activity. The lava lake formed during this period has remained active to this day, making Erta Ale one of the few volcanoes in the world with a persistent lava lake.
The 1967 Eruption
Erta Ale’s activity gained significant scientific interest during the 1967 eruption. This eruption further established the volcano as a continuous basaltic shield volcano, drawing attention from volcanologists and geologists worldwide. The 1967 eruption highlighted the volcano’s unique characteristics, including its low-viscosity basaltic lava flows and persistent summit lava lake.
The 2005 Eruption
In November 2005, Erta Ale experienced a notable eruption that resulted in new fissure openings on the volcano’s flank. This eruption led to significant lava flows that extended several kilometers from the summit. The 2005 eruption emphasized the dynamic nature of Erta Ale, as new fissures and lava flows altered the landscape around the volcano.
Scientific Significance
Research and Observations
Volcanological Studies
Erta Ale’s continuous activity has made it a focal point for volcanological studies. Researchers from around the world have conducted extensive studies to understand the behavior of its lava lake, the dynamics of its eruptions, and the structural evolution of the volcano. Studies on Erta Ale have contributed significantly to the understanding of shield volcanoes and their eruption patterns, especially in the context of the East African Rift.
The volcano’s lava lake is of particular interest. It is one of the few permanent lava lakes in the world, providing a rare opportunity for continuous observation. Researchers have studied the lake’s temperature, composition, and gas emissions to gain insights into the underlying magma chamber and its dynamics. These observations help in understanding the degassing processes and the thermodynamics of basaltic lava lakes.
Geological Insights
Erta Ale’s geological characteristics offer a window into the tectonic activities of the region. The volcano is located in the Danakil Depression, one of the Earth’s lowest and hottest places, formed due to the divergence of the African and Arabian tectonic plates. This unique setting allows scientists to study rift dynamics and the formation of new oceanic crust.
The frequent fissure eruptions at Erta Ale provide insights into the formation and evolution of fissure-fed lava flows. By studying these flows, scientists can understand the processes that lead to the formation of new crust and the role of magma in shaping the landscape. These studies are crucial for understanding the broader implications of rift tectonics and volcanic activity.
Monitoring Efforts
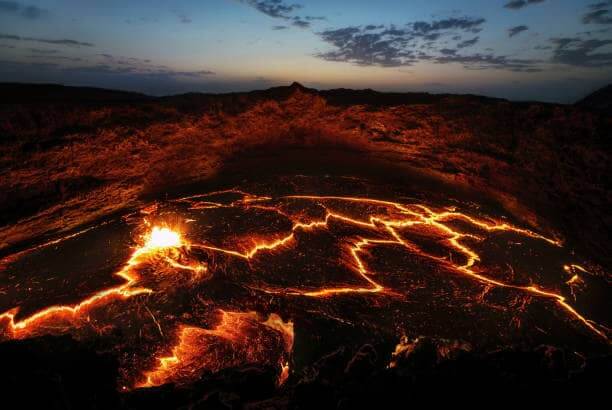

Satellite Monitoring
Satellite imagery and remote sensing technologies play a vital role in monitoring Erta Ale. Thermal anomalies detected by satellites provide real-time data on the temperature changes in the lava lake and the surrounding area. This data helps in predicting potential eruptions and understanding the thermal dynamics of the volcano.
Ground-Based Observations
Ground-based observations complement satellite data by providing detailed information on the volcano’s surface activities. Researchers and volcanologists regularly visit Erta Ale to conduct field studies, collect samples, and observe the lava lake’s behavior. These observations are crucial for validating satellite data and gaining a comprehensive understanding of the volcano’s activities.
Seismic Monitoring
Seismic monitoring is another critical aspect of studying Erta Ale. Seismographs installed around the volcano detect and record seismic activities, which are often precursors to eruptions. By analyzing these seismic signals, scientists can predict potential eruptions and understand the movement of magma beneath the surface.
Visiting Erta Ale
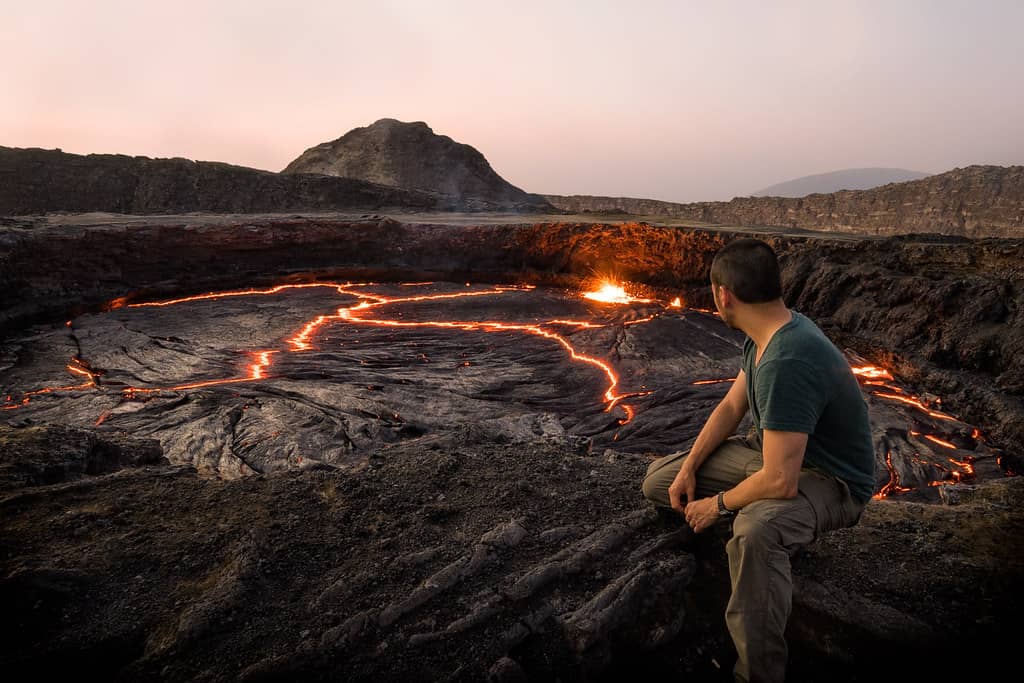

Travel Tips
Best Time to Visit
The best time to visit Erta Ale is during the cooler months, from November to February. The temperatures in the Danakil Depression can soar during the summer, making the trek to the volcano challenging and uncomfortable. During the cooler months, temperatures are more manageable, allowing for a more pleasant experience.
Necessary Permits
Before embarking on your journey to Erta Ale, it’s crucial to secure the necessary permits. The region is closely monitored due to its geological significance and proximity to the Ethiopian-Eritrean border. Working with a reputable tour operator can help streamline this process, ensuring all required permits and documentation are in order.
Choosing a Tour Operator
Selecting a reliable tour operator is vital for a successful trip to Erta Ale. Look for operators with positive reviews and extensive experience in organizing tours to the volcano. They will provide essential services such as transportation, guides, and necessary equipment, ensuring your safety and comfort throughout the journey.
Packing Essentials
Pack appropriately for the harsh conditions of the Danakil Depression. Essential items include:
- Sturdy hiking boots: The rocky terrain requires durable footwear for a safe trek.
- Light, breathable clothing: The hot climate demands lightweight and moisture-wicking fabrics.
- Sun protection: Bring sunglasses, a wide-brimmed hat, and high-SPF sunscreen to protect against the intense sun.
- Water and snacks: Staying hydrated is crucial, so carry ample water and high-energy snacks.
- Camping gear: If your tour involves an overnight stay, ensure you have a good quality sleeping bag and tent.
Safety Considerations
Guided Tours
Always visit Erta Ale with an experienced guide. Guides are knowledgeable about the terrain, volcanic activity, and safety protocols, ensuring that you are well-informed and protected during your visit. They can provide crucial insights into the volcano’s behavior and navigate the safest paths.
Monitoring Volcanic Activity
Before and during your trip, stay updated on the volcano’s activity. The Global Volcanism Program and other monitoring agencies provide real-time data on volcanic activity. Your tour operator should also be aware of current conditions and make necessary adjustments to your itinerary if needed.
Emergency Preparedness
Familiarize yourself with the emergency procedures and evacuation routes. In case of sudden volcanic activity, it’s essential to know how to respond quickly and effectively. Your guide will brief you on these protocols, but it’s crucial to remain vigilant and aware of your surroundings at all times.
Respecting Local Communities
Erta Ale is located in the Afar region, home to the Afar people. Show respect for their customs and traditions. Engage with the local community through your tour operator, and support local businesses where possible. This not only enhances your travel experience but also contributes positively to the region’s economy.
Conclusion
Visiting Erta Ale Volcano is a unique and thrilling adventure, offering a rare glimpse into one of Earth’s most active volcanic sites. From understanding its geological significance to preparing for the trek with practical travel tips, this guide aims to ensure a safe and memorable experience. Whether you’re drawn by the scientific allure of its continuous lava lake or the sheer excitement of exploring a natural wonder, Erta Ale stands as a testament to the powerful forces shaping our planet. With proper planning and respect for the local environment and communities, your journey to this fiery gateway will undoubtedly be an unforgettable highlight of your travels in Ethiopia.
Frequently asked questions
-
Where is Erta Ale located?
Erta Ale is located in the Afar region of Ethiopia, near the Danakil Depression, known for its volcanic and geothermal activities.
-
What are some distinctive features of Erta Ale?
Erta Ale is characterized by its active lava lake, fissures, and occasional flank eruptions, making it one of the most active volcanoes in Ethiopia.
-
How long has Erta Ale been active?
Erta Ale has been active since at least 1967, with historical records suggesting possible activity as early as 1906.
-
What is the significance of Erta Ale in global volcanism?
Erta Ale is monitored by the Global Volcanism Program due to its consistent volcanic activity, providing valuable insights into magmatic processes.
-
What is the elevation of Erta Ale?
Erta Ale's summit sits at an elevation of about 613 meters above sea level, making it one of the few high-elevation lava lakes.
About Author
Meet Hanan Akmel, our SAAS SEO Specialist with a rich experience of 5 years in enhancing online presence for diverse clients. With a passion for digital landscapes and a keen eye for search engine trends, Hanan excels in crafting strategies that significantly boost search engine rankings and user engagement. Her expertise lies in seamlessly integrating technical SEO with content-driven approaches, ensuring a holistic growth for her clients’ digital footprint.
Subscribe to stay up-to-date with Ethiopia
Get the Free monthly newsletter